Multimodal Reasoning
Advancing abnormality grounding via Vision-Language Models.
Scientific Thesis
Open Challenges
Multimodal Anomaly Grounding
Anchor visually detected anomalies in structured clinical language, ensuring that explanations correspond to anatomically and pathophysiologically valid concepts rather than free-form descriptions.
Language-Conditioned Generation and Repair
Develop generative models that can be steered by semantic constraints, enabling hypothesis-driven synthesis, counterfactual reasoning, and targeted normalization guided by clinical language.
Open-World Reasoning
Enable vision–language systems to reason about unseen anomalies, supporting interpretation of rare, ambiguous, or previously uncharacterized findings.
Key Publications
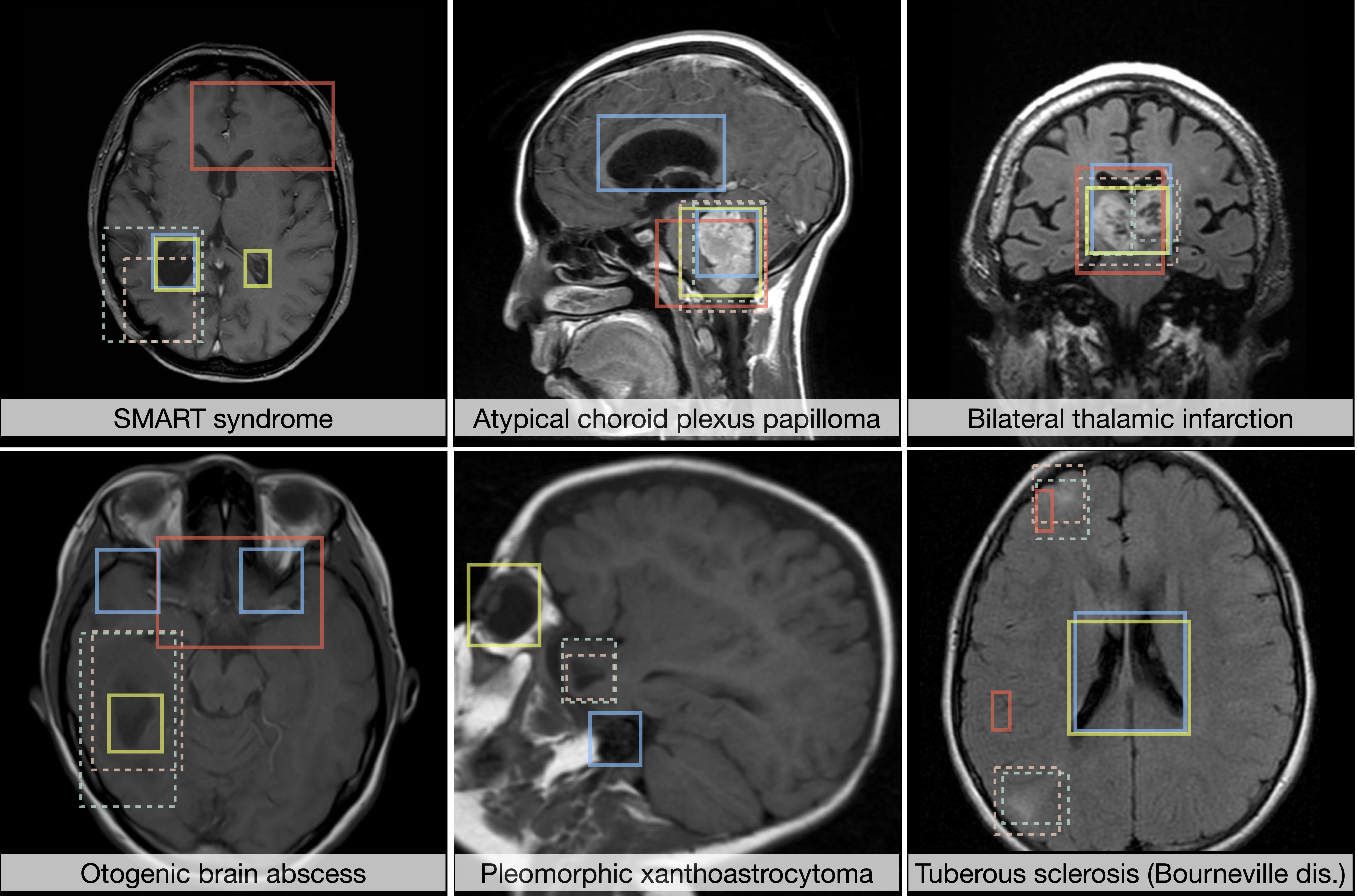
NOVA: A Benchmark for Rare Anomaly Localization and Clinical Reasoning in Brain MRI
Cosmin I. Bercea, Jun Li, Philipp Raffler, Evamaria O. Riedel, Lena Schmitzer, Angela Kurz, Felix Bitzer, Paula Roßmüller, Julian Canisius, Mirjam L. Beyrle, Che Liu, Wenjia Bai, Bernhard Kainz, Julia A. Schnabel, Benedikt Wiestler
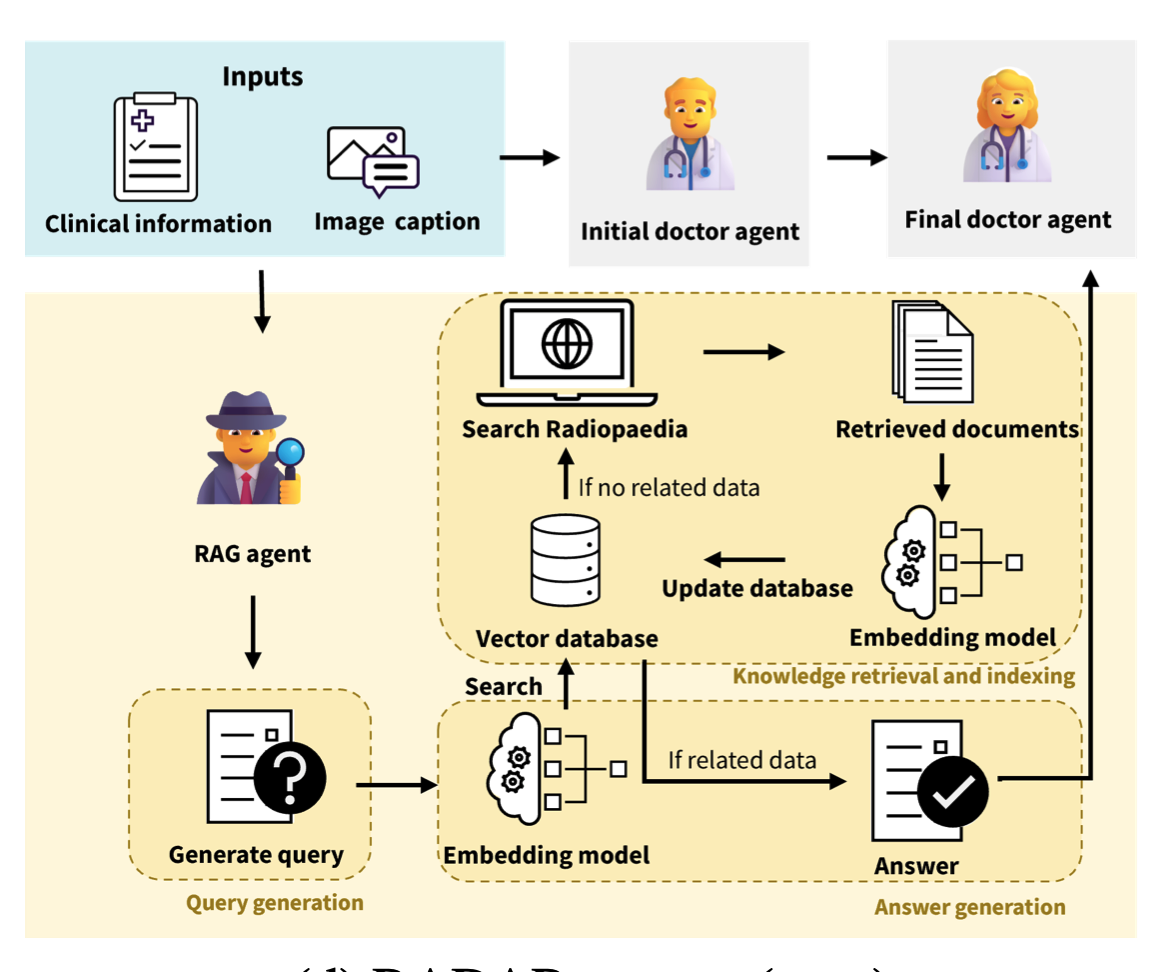
Learning to Reason about Rare Diseases through Retrieval-Augmented Agents
Ha Young Kim, Jun Li, Ana Beatriz Solana, Carolin M. Pirkl, Benedikt Wiestler, Julia A. Schnabel*, Cosmin I. Bercea*
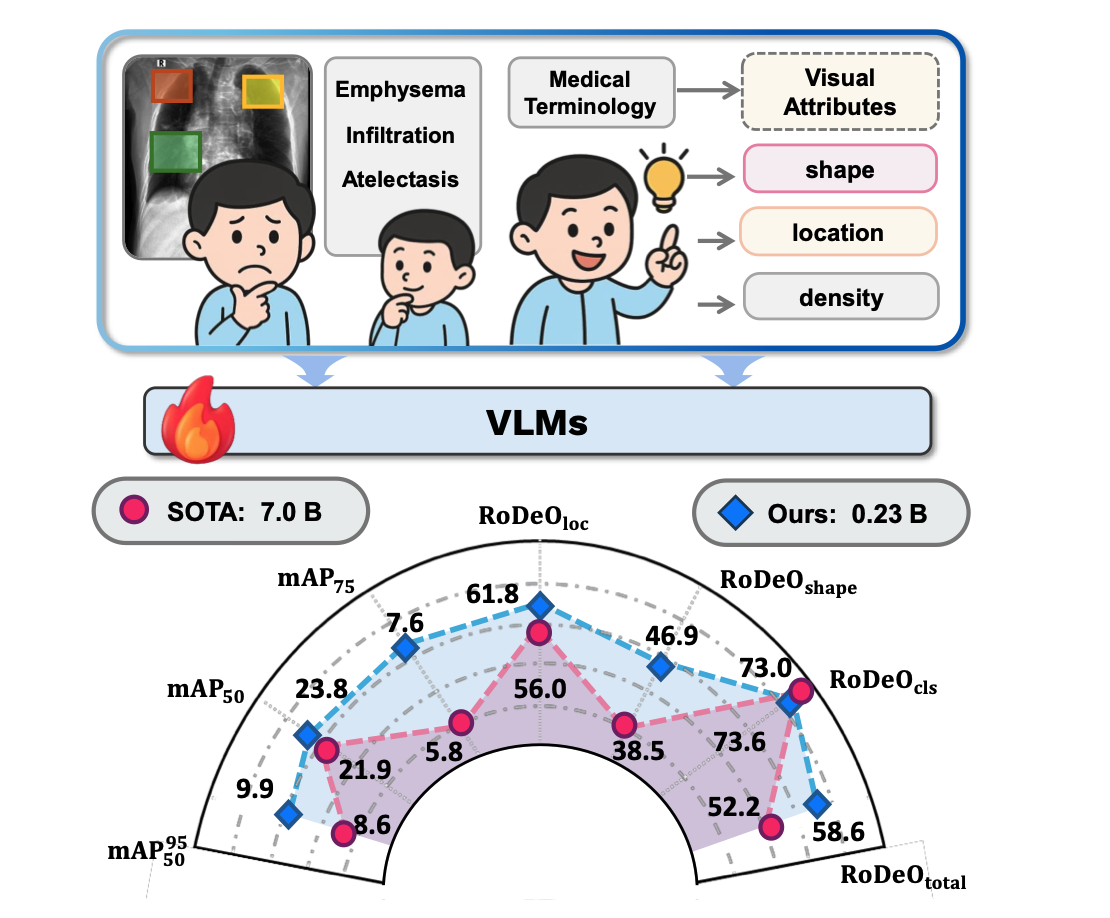
Enhancing Abnormality Grounding for Vision-Language Models with Knowledge Descriptions
Jun Li, Che Liu, Wenjia Bai, Rossella Arcucci, Cosmin I. Bercea*, Julia A. Schnabel*
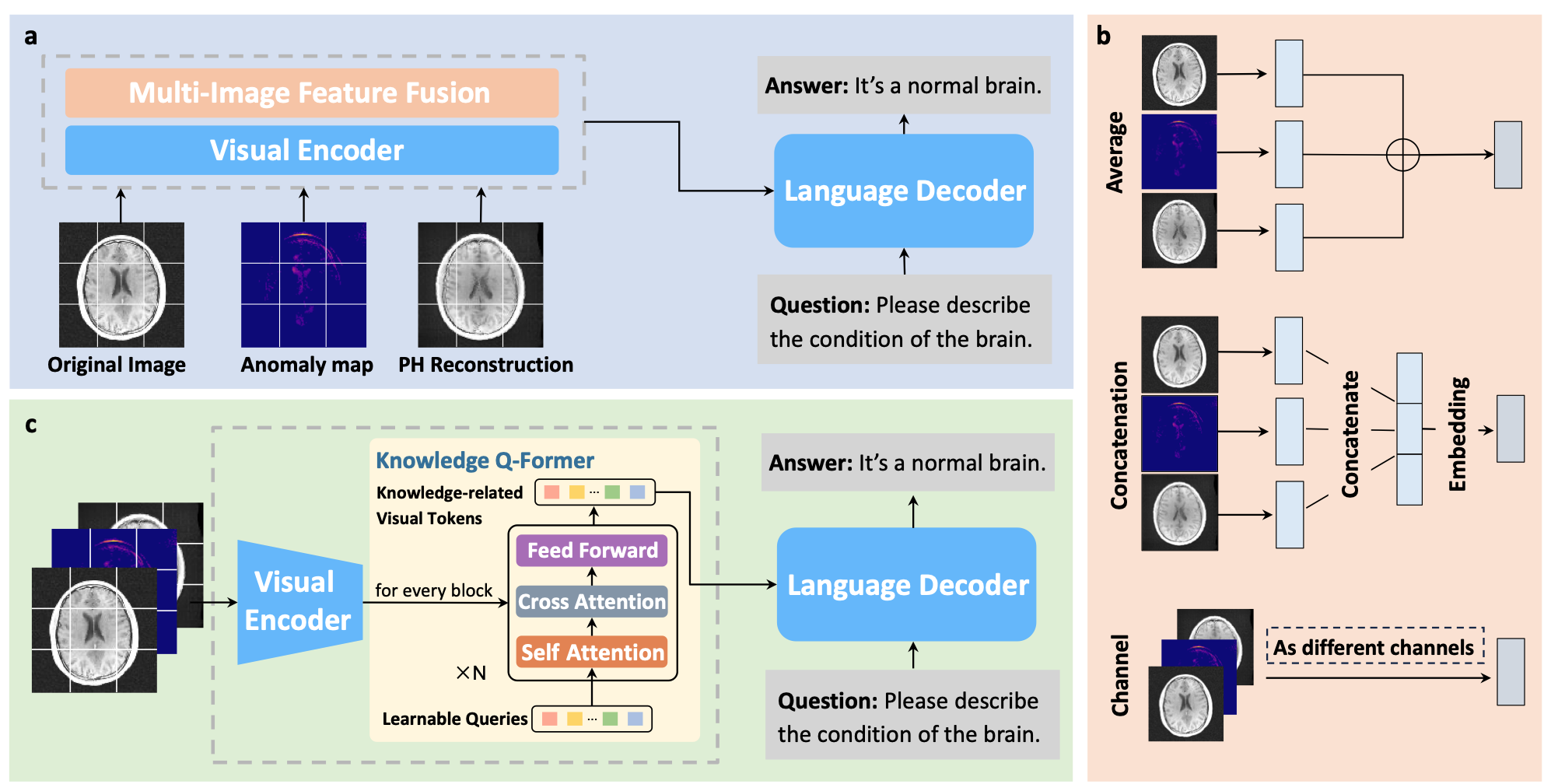
Language Models Meet Anomaly Detection for Better Interpretability and Generalizability
Jun Li, Su Hwan Kim, Philip Müller, Lina Felsner, Daniel Rückert, Benedikt Wiestler, Julia A. Schnabel*, Cosmin I. Bercea*